Viable cell density monitoring in bioreactor
Introduction
Monitoring cell density and viability of mammalian cell culture bioreactors is a necessary task that present today a number of remaining challenges. Traditional measure for cell count and cell viability still relies on sampling and staining protocol where the trypan blue exclusion method is performed once a day. While automatic cell counters have reduced the statistical error of the original manual method, daily sampling is still a challenge for small scale bioreactor because the sampled volume becomes significant. NORMA analyzers integrate a new breakthrough method for accurately determination of cell concentration and viability without staining nor sample preparation or dilution. Two comparative studies between our NORMA XS and one of the reference methods showed the close correlation between our device and the reference counters. A first one concerning the NORMA XS and the Beckman Coulter Vi-Cell XR on the perfusion and fed-batch processes; and a second one comparing in parallel the NORMA XS, the Vi-Cell XR and the Nova BioProfile FLEX on 12 fed-batch bioreactors. Moreover, we assess the very high reproducibility of such technique with a low sample volume of 3 μL.

Material & methods
The NORMA XS is very easy to use: the sample is simply placed on the measuring area of the slide without dilution or labelling. Then, the technology directly acquires the light diffraction properties of each individual cells through their hologram images without any settings. Several thousands of holograms are acquired into one single image that is immediately “reconstructed” with holographic algorithm to obtain a microscopic like picture; at this stage cells can be segmented. Living and dead cells have significant holographic patterns that can be distinguished and accurately counted.
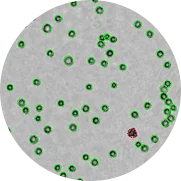
Zoom of a CHO cell image with superposition of the detection mask and viability determination
Green circles (viable cells)
Red circles (dead cells)
Results
A strong correlation between the NORMA XS and the Beckman Coulter Vi-Cell XR on the perfusion and fed-batch processes
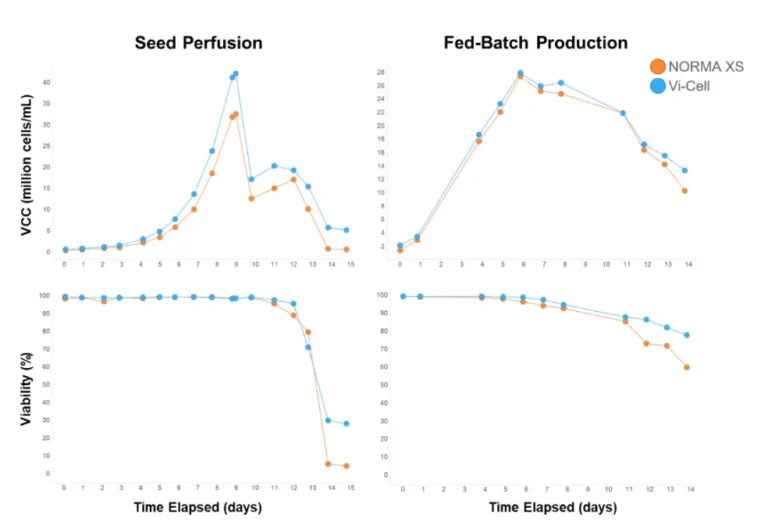
A first comparative study between the Beckman Coulter Vi-Cell XR and our NORMA XS was realised on CHO cells on two different processes: the perfusion and fed-batch mode. A measurement was performed every day on the NORMA XS and Vi-Cell XR, except week-ends for the fed-batch run (day 2, 3, 9 and 10 on the graph in figure 2). The results showed that NORMA XS trended close to the reference method Vi-Cell XR for VCC (Viable Cell Count) up to 40×10^6 cells/mL and viability from 0 to 100% for both perfusion and fed-batch processes (Figure 1).
Figure 1 : The NORMA XS versus the Vi-Cell XR Evaluation on perfusion and fed-batch processes (data courtesy of GSK)
Acknowledgement : These results are part of a project that has received funding from the Innovative Medicines Initiative 2 Innovative Medicines Initiative 2 Joint Undertaking (grant agreement No 777397 for funding. This Joint Undertaking receives the support from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme and EFPIA partners Bayer, Byondis , GSK, Pfizer, Rentschler Biopharma, Sanofi and UCB.
ihi.europa.eu
Disclaimer : This communication reflects the author’s view and neither IMI nor the European Union, EFPIA, or any Associated Partners are responsible for any use that may be made of the information contained therein.




The Viable Cell Density and cell viability correlation between the Nova BioProfile FLEX, Beckman Coulter Vi-Cell XR and NORMA XS on 12 parallel fed-batch bioreactors
A second comparative survey between the Nova BioProfile FLEX, Beckman Coulter Vi-Cell XR and the NORMA XS was performed using 12 parallel fed-batch bioreactors up to a concentration of 15 million CHO cells. This concentration range didn’t allow the NORMA XS performance to be pushed to its maximum, so we concentrate samples by 2 and by 4 to reach around 30 and 40×10^6 cells/mL (Figures 2A and 3A).In the case of Vi-Cell XR versus NORMA XS test, with a concentration range up to 40×10^6 cells/mL and viability range at 75-100%, we obtained a correlation factor of 0.98 between the two compared methods. The large field of view allows the analysis of several thousand cells within a single image, keeping the statistical variability of the measure as low as 3% (Figure 2).In the case of BioProfile FLEX versus NORMA XS test, we found a ratio of approximately 1.043 between the two measurements and a coefficient of determination R2 of approximately 0.95 with a cell density ranging from 0.2×10^6 to 30×10^6 cells/ml (Figure 3A). Moreover, with a cell viability ranging from 0 to 100%, we found a ratio of approximately 1.01 between the two measurements and a coefficient of determination R2 of approximately 0.99 (Figure 3B).
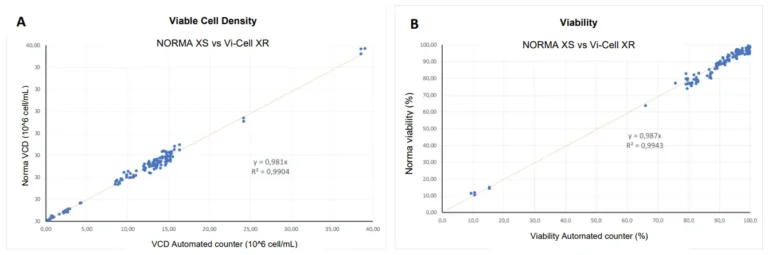
Figure 2 : Viable cell density (A) and cell viability (B) correlation between the lensless imaging technique NORMA XS and the trypan blue reference instrument Beckman Coulter Vi-Cell, for N=84
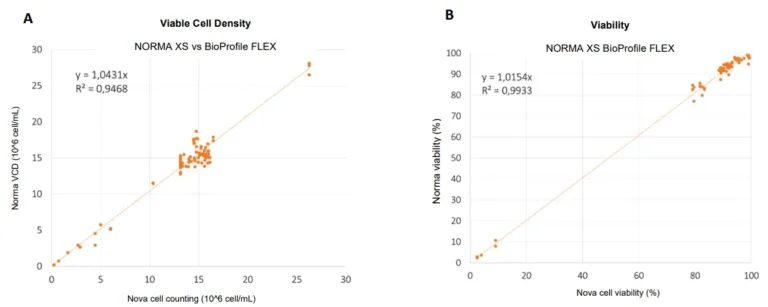
Figure 3 : Viable cell density (A) and cell viability (B) correlation between the lensless imaging technique NORMA XS and the trypan blue reference instrument Nova BioProfile FLEX, for N=84
High reproducibility of the NORMA XS
Moreover, we assessed the repeatability of our method with two tests. First, we measured the same sample 12 times with the same NORMA XS; and then, we measured one sample on several NORMA XS. These tests can therefore affirm the very good repeatability of our devices.
REPEATABILITY | CV (%) |
|---|---|
Single sample injected in 12 different chambers and measured with 1 NORMA XS | 3.23 |
Single sample injected in 1 chamber and measured with 5 separate NORMA XS | 3.54 |
Conclusion
Acknowledgements
iConsensus consortium
The project leading to this application has received funding from the Innovative Medicines Initiative 2 Joint Undertaking under Grant Agreement n°777397. This Joint Undertaking receives the support from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme and EFPIA.
References
(1) C. Allier, T. Bordy, et al., “Label-free cell viability assay using lens-free microscopy”
(2) G. Esteban, M. Pisaneschi, J. Cubeta and D. Sergeant, “Viable cell density monitoring in bioreactor with lensless imaging”, ESACT conference 2017 poster
(3) G. Esteban, M. Hill, « Viable Cell Density and Viability in High-Throughput Cell Culture Applications”, Cambridge Healthtech Institute Webinar 2020
